
In today’s rapidly changing world, environmental management has become an integral part of any responsible business strategy. Organizations across various industries are recognizing the significance of adopting environmentally friendly practices to minimize their ecological footprint and ensure sustainability. One key tool that aids in achieving these goals is an Environmental Management Plan (EMP). In this article, we will explore what an EMP is, why it is important, and how its implementation can contribute to a greener future.
Understanding Environmental Management Plan (EMP)
An Environmental Management Plan (EMP) is a strategic framework developed by organizations to systematically identify, assess, and manage environmental impacts associated with their operations, products, or services. It provides a structured approach to environmental stewardship, allowing businesses to align their practices with regulatory requirements, industry standards, and community expectations.

An effective EMP involves a comprehensive analysis of an organization’s activities, including resource consumption, waste generation, emissions, and ecological impact. By evaluating these factors, businesses can identify areas for improvement, set targets, and establish actionable measures to mitigate adverse effects on the environment.
The Importance of Environmental Management Plans (EMPs)
1. Regulatory Compliance and Risk Mitigation
In an era of increasing environmental regulations, adherence to legal requirements is essential for organizations to avoid penalties, litigation, and damage to their reputation. Implementing an EMP helps companies stay compliant with relevant environmental Management systems l laws and regulations, reducing the risk of non-compliance and associated consequences.
2. Reputation and Stakeholder Trust
Consumers today are becoming more conscious of the environmental impact of the products and services they choose. By embracing sustainable practices and clearly demonstrating their commitment to environmental stewardship through an EMP, businesses can enhance their reputation, gain a competitive edge, and build trust among stakeholders.
3. Cost Reduction and Efficiency

Effective environmental management can lead to significant cost savings through improved resource utilization, waste reduction, and energy efficiency. An EMP enables organizations to identify opportunities for optimization, implement sustainable technologies and practices, and achieve operational efficiencies that translate into long-term financial benefits.
4. Environmental Conservation and Sustainable Development
One of the primary goals of an EMP is to minimize negative impacts on the environment audits and promote sustainable development. By implementing environmentally friendly practices, organizations contribute to the preservation of ecosystems, biodiversity, and natural resources, fostering a greener and healthier planet for future generations.
Implementing an Environmental Management Plan (EMP)
Developing and implementing an EMP requires a systematic and collaborative approach within an organization. Here are some essential steps to consider:
1. Environmental Assessment
Conduct a comprehensive assessment of your organization’s environmental impact, including resource consumption, waste generation, emissions, and potential ecological risks. Identify areas that require immediate attention and prioritize actions based on their significance and feasibility.
2. Set Goals and Targets
Establish measurable goals and targets that align with your organisation’s overall environmental objectives. These targets should be specific, achievable, and time-bound, allowing for progress tracking and continuous improvement.
3. Action Planning
Develop an action plan that outlines the specific initiatives, strategies, and activities required to achieve the established goals. Assign responsibilities, allocate resources, and set realistic timelines for implementation.
4. Monitoring and Evaluation
Regularly monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of your EMP by measuring key performance indicators (KPIs) related to environmental impact. This will enable you to track progress, identify areas for improvement, and make informed decisions for ongoing optimization.
Communication and Stakeholder Engagement
Engage internal and external stakeholders in the environmental management process. Foster a culture of environmental responsibility among employees, collaborate with suppliers and partners who share similar values, and communicate your organization’s environmental initiatives to customers, shareholders, and the wider community.
By adopting an Environmental Management Plan (EMP), organizations can proactively address environmental challenges and drive positive change. An EMP not only ensures regulatory compliance but also strengthens the organization’s reputation, reduces costs, and contributes to the conservation of our planet. Let us embrace sustainability and work together towards a greener future.
Implementing an Environmental Management Plan (EMP) requires a dedicated commitment from the organization and its stakeholders.
1. Training and Awareness
Invest in training programs to raise awareness among employees about environmental issues and the importance of sustainable practices. By providing education and resources, you empower your workforce to actively participate in environmental management efforts.
2. Continuous Improvement
Environmental management is an ongoing process that requires continuous improvement. Regularly review and update your EMP to incorporate new technologies, industry best practices, and changing regulations. Stay informed about advancements in sustainability and adapt your strategies accordingly.
3. Collaboration and Partnerships
Collaborate with industry peers, environmental organizations, and government bodies to share knowledge and experiences. Participate in sustainability initiatives and join forums or associations that promote environmental responsibility. You can leverage collective expertise to address common challenges and drive innovation by forming partnerships.
4. Life Cycle Assessment
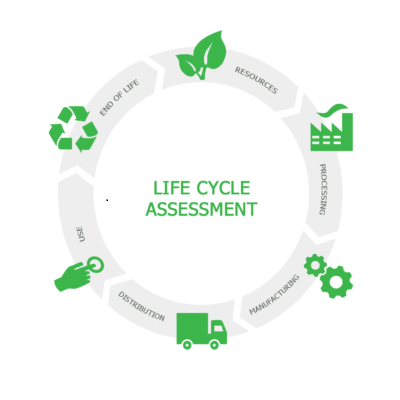
Consider conducting a life cycle assessment (LCA) to evaluate the environmental impact of your products or services from production to disposal. This holistic approach allows you to identify hotspots and areas where improvements can be made at different stages of the product life cycle.
5. Reporting and Transparency
Transparently communicate your organization’s environmental performance and progress to stakeholders through sustainability reports. Include relevant data, targets, and achievements, highlighting the positive impact of your EMP. This transparency builds trust and demonstrates accountability.
Conclusion
An Environmental Management Plan (EMP) serves as a roadmap for organizations to navigate the challenges of environmental sustainability. By implementing an effective EMP, businesses can ensure regulatory compliance, enhance their reputation, reduce costs, and contribute to the preservation of our planet. Remember, the journey towards environmental stewardship requires continuous effort, collaboration, and a shared commitment to a greener future.




